Brain Type 13 - Your Brain's Amazing Workings
Have you ever stopped to consider what is really happening inside your head? It’s a pretty busy place, as a matter of fact. Every single second, your brain is doing so much, handling all sorts of jobs, from remembering what you had for breakfast to helping you feel happy or sad. It’s like a central command center for everything you do and experience, and it’s truly remarkable how it all works together, you know?
This incredibly complex part of you is what allows you to think, to hold on to memories, and to feel a whole range of emotions. It also helps you move your body, see the world around you, and even manage things like your breathing and how warm or cold you feel. Basically, it’s behind every single process that keeps your body going, which is quite something, really.
When we talk about something like "brain type 13," we are, in a way, just trying to better understand the many different forms this incredible organ can take and how its core operations might express themselves uniquely in each person. It’s a way of looking at the amazing variety in how our inner workings shape who we are, and how we interact with our surroundings, too it's almost.
Table of Contents
- The Brain's Central Role
- How Does Your Brain Type 13 Process Information?
- The Brain's Parts and Their Purpose
- What Happens to Your Brain Type 13 as You Get Older?
- Keeping Your Brain Type 13 Healthy
- How Does Brain Type 13 Influence Our Daily Lives?
The Brain's Central Role
Your brain, quite simply, is the main spot for your body's control system. It's the big mass of nerve tissue that sits up front in your head, really. For all creatures with a backbone, and even most without, this is where the nervous system has its headquarters. It’s a collection of nervous material, and you’ll typically find it tucked away in the head, naturally.
This remarkable organ is always busy, taking in all the bits of information your senses gather. Think about it: when you touch something, see a color, hear a sound, or even smell something cooking, your brain is the one putting all those pieces together. Then, after it figures out what’s going on, it tells your body what to do next, like moving your hand away from something hot, or perhaps turning your head to listen more closely. It’s a rather fast and efficient system, you know?
For creatures that are a bit more developed, like us, the brain does so much more than just react. It’s where our deeper thoughts happen, where we can plan ahead, and where we make sense of the world in more complicated ways. It’s almost like a super-smart director, guiding the entire show, you see.
How Does Your Brain Type 13 Process Information?
The main job of your brain, regardless of whether we are talking about a "brain type 13" or any other way of thinking about brains, is to manage the flow of messages throughout your central nervous system. These messages are like tiny bits of information, sent and received constantly. They are what tell your body what’s happening, what to feel, and what to do. It’s a pretty busy highway of signals, basically.
These signals, you know, carry all the information from your five senses. So, when you look at something, the signals from your eyes go to your brain. When you hear a sound, the signals from your ears make their way there, too. The same goes for smells, tastes, and anything you touch. Your brain takes all this incoming sensory data and makes sense of it, turning raw information into what you actually experience, which is really quite amazing.
It’s also responsible for sending out its own messages. When you decide to pick up a cup, your brain sends signals to your muscles telling them to move. When you feel hungry, your brain is involved in sending signals that create that feeling. This back-and-forth communication is happening all the time, quite literally, keeping you connected to your body and the world around you, as a matter of fact.
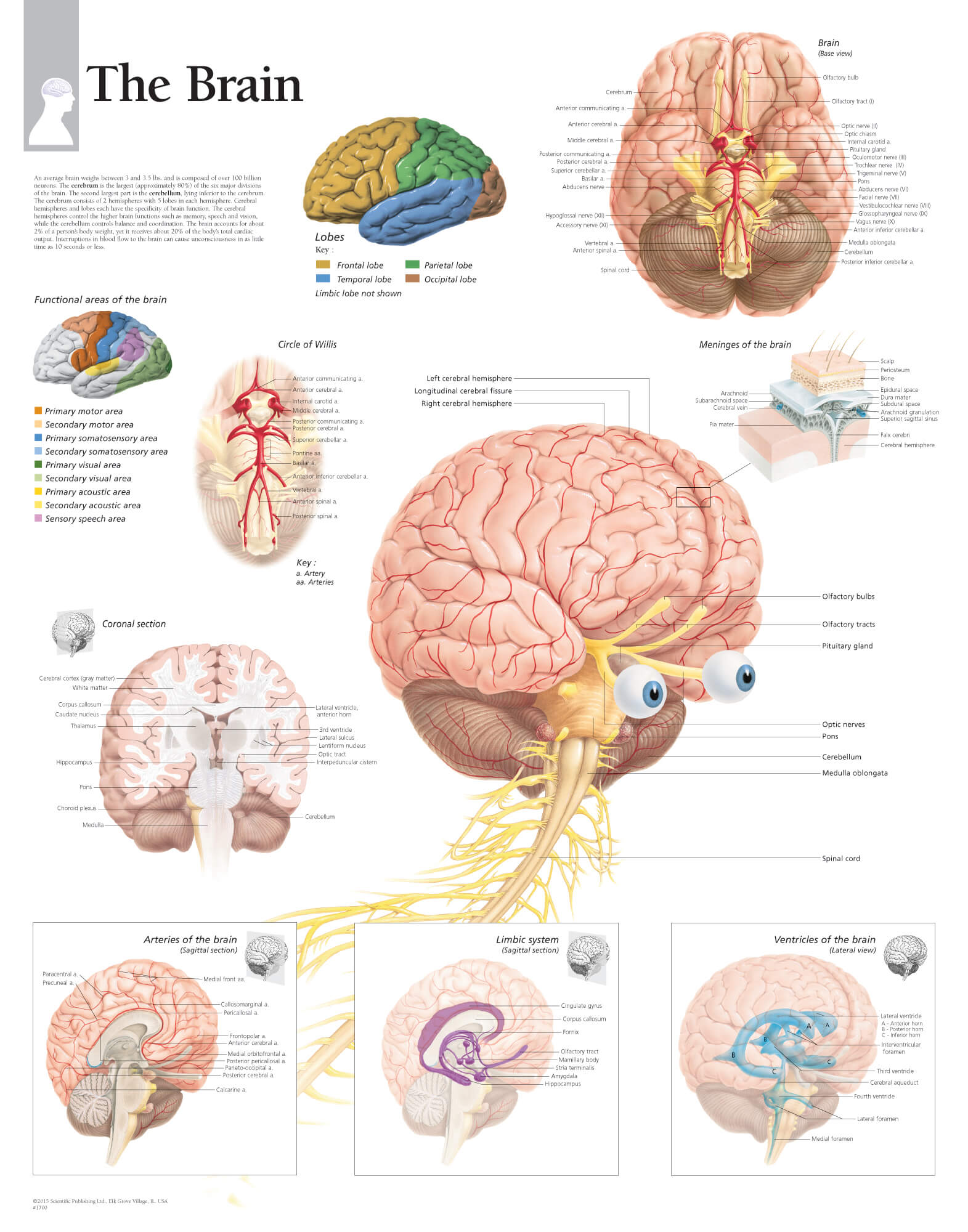
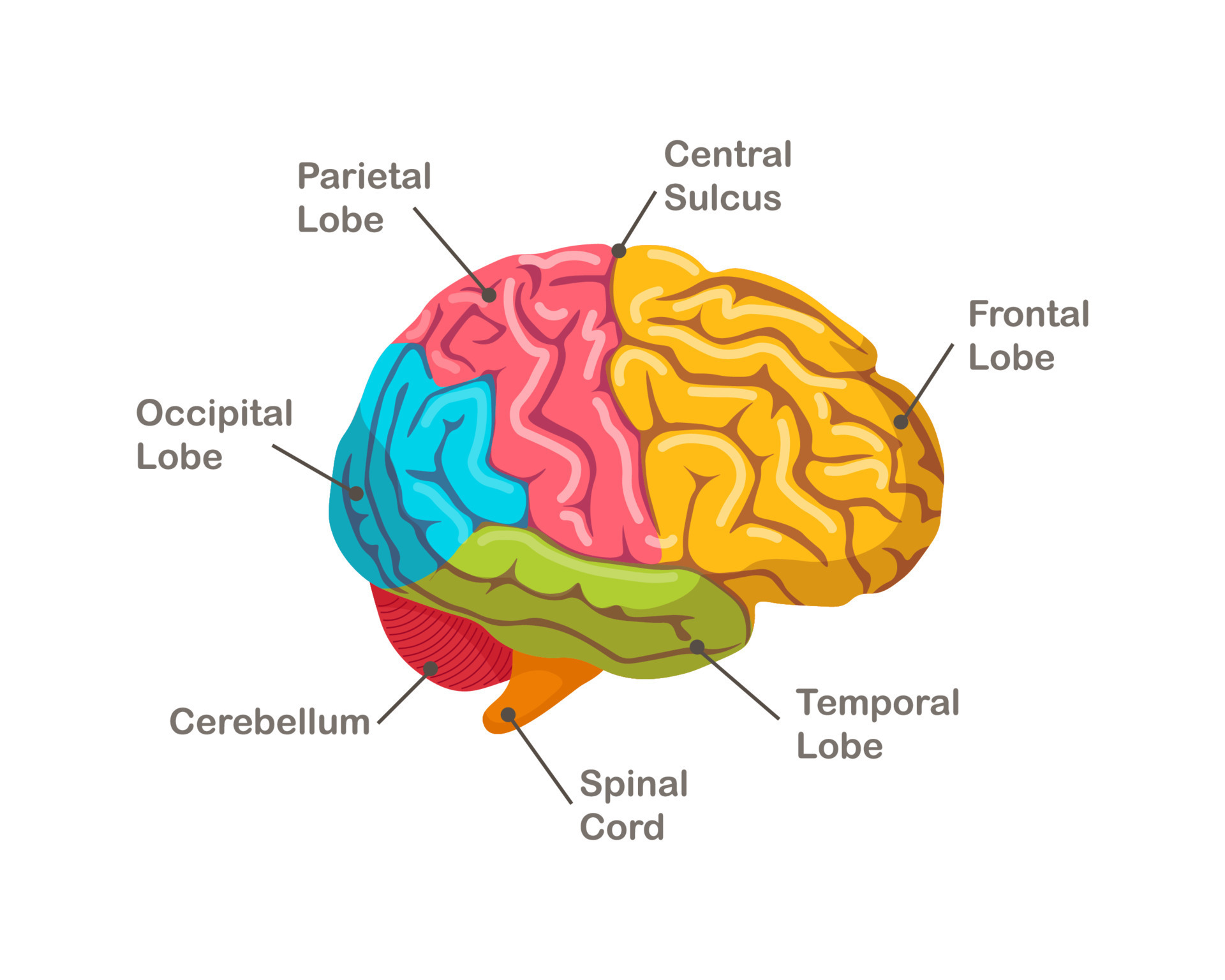
The Brain's Parts and Their Purpose
The human brain is, you could say, a rather intricate organ, put together from several distinct sections. Each one of these sections has its own set of jobs, and they all work together to make your brain function as a whole. It’s like a well-coordinated team, where every player has a role, naturally.
The Cerebrum and Brain Type 13
The cerebrum, for instance, is the largest part of your brain. It’s the big, wrinkled part you often see pictures of. This part is responsible for a lot of your higher-level thinking. It’s where your sensory information is processed, like when you feel the warmth of the sun or see the blue sky. It’s also where you do your conscious thinking, planning, and where your memories are stored, too it's almost.
When we think about a "brain type 13," the cerebrum would be a significant part of what shapes its unique characteristics. How it processes sensory input, how it forms thoughts, and how it handles memory could all contribute to what makes one brain slightly different from another. It’s where a lot of what makes you, you, really comes from, you know?
The Cerebellum and Its Contribution to Brain Type 13
Then there’s the cerebellum, which is a smaller part located at the back of your brain, underneath the cerebrum. While it might be smaller, its role is quite important. The cerebellum is mostly about coordination and balance. It helps you move smoothly, whether you’re walking, running, or just reaching for something. It makes sure your movements are fluid and controlled, which is pretty essential for daily life, you see.
For a "brain type 13," the cerebellum's efficiency in coordinating movements and maintaining balance could influence physical abilities and how one interacts with their physical environment. A well-tuned cerebellum, for instance, might mean a person is more graceful or has better fine motor control. It’s a part that works quietly behind the scenes, but its impact is felt in almost every physical action, naturally.
The Brain Stem and Brain Type 13's Basic Functions
Finally, we have the brain stem. This is the part that connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to your spinal cord. It’s like the control center for all the automatic stuff your body does without you even thinking about it. Things like your breathing, your heart beating, your body temperature, and even your sleep cycle are all managed by the brain stem. It’s pretty vital for just keeping you alive and functioning, basically.
When considering a "brain type 13," the brain stem ensures that all the fundamental life-sustaining processes are running smoothly. While it doesn't directly influence personality or complex thought, its stable operation provides the necessary foundation for all other brain functions. Without a healthy brain stem, none of the other amazing things your brain does would even be possible, you know?
What Happens to Your Brain Type 13 as You Get Older?
Just like the rest of your body, your brain changes over time. As the years go by, you might notice some shifts in how your brain works. For instance, the overall size or mass of the brain can decrease a little with age. Also, the connections between brain cells, which are called synaptic connections, can become fewer. These are natural parts of the aging process, you see.
These changes can sometimes lead to a slight decline in certain cognitive abilities. Things like how quickly you can recall a name or how easily you can learn something new might not be quite as sharp as they once were. This doesn't mean your brain stops working well, just that it might operate a little differently. It’s a very common part of getting older, naturally.
When we think about a "brain type 13," these age-related changes would apply to it just as they do to any brain. How a specific "brain type" adapts to these changes, or how quickly they might occur, could be an interesting area to consider, though the basic mechanisms of aging are pretty universal, as a matter of fact.
Keeping Your Brain Type 13 Healthy
Since your brain is so important, it makes sense to try and keep it in good shape. There are many simple things you can do that really help. Staying physically active, for example, is great for your brain. Exercise helps blood flow, which brings important things like oxygen and nutrients to your brain cells, you know.
What you eat also makes a big difference. A diet full of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can support brain health. Getting enough sleep is another huge factor; it allows your brain to rest and sort through all the information from the day. And keeping your mind active, by learning new things or solving puzzles, can also help keep your brain sharp, basically.
For any "brain type," including "brain type 13," these healthy habits are truly beneficial. They help maintain the billions of nerve cells and their complicated connections, which are arranged in patterns that help coordinate everything from your thoughts and feelings to your movements and sensations. It’s like giving your brain the best possible environment to do its amazing work, you see.
How Does Brain Type 13 Influence Our Daily Lives?
Every single thought, every belief you hold, all your memories, the way you act, and even your moods, all come from inside your brain. It truly is the place where thought and intelligence happen, and it acts as the main control point for your entire body. So, when we talk about a "brain type 13," we are really talking about how these fundamental brain functions might combine to create a particular way of experiencing the world, naturally.
The brain holds an incredible number of nerve cells, literally billions of them, arranged in what you could call a complicated highway system. These cells are set up in specific patterns that work together to manage your thoughts, your emotions, your behaviors, how you move, and what you sense. It’s this intricate network that allows you to interact with the world and express yourself, you know?
So, considering something like a "brain type 13" means looking at how this complex internal system expresses itself in a person's day-to-day existence. It's about how the unique combination of these functions shapes how someone thinks, feels, and acts, making each individual truly distinct, you see.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/brain_activity-5798eebf5f9b589aa9ae69b2.jpg)
Anatomy of the Brain: Structures and Their Function
The Brain | Scientific Publishing
Sections of human brain. Anatomy. Side view of organ 10200247 Vector